
Bernoulli argued that any sonorous body could vibrate in a series of simple modes with a well-defined frequency of oscillation.
Principle of superposition code#
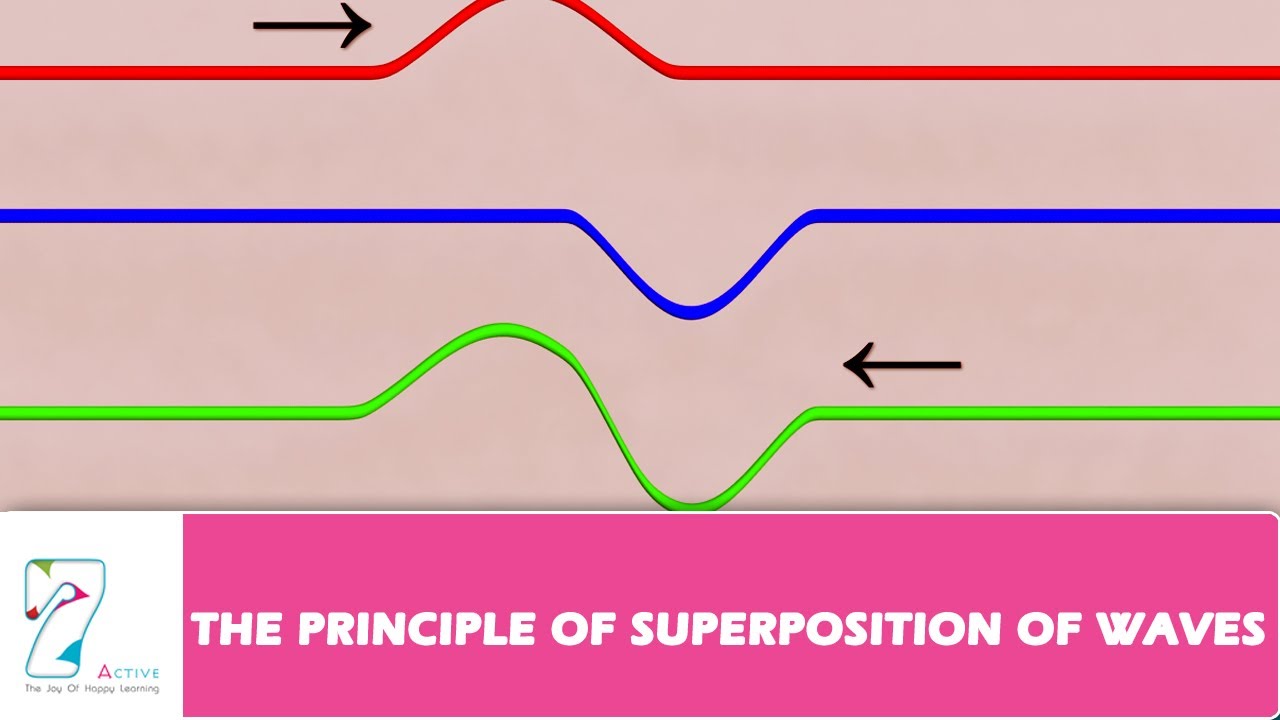
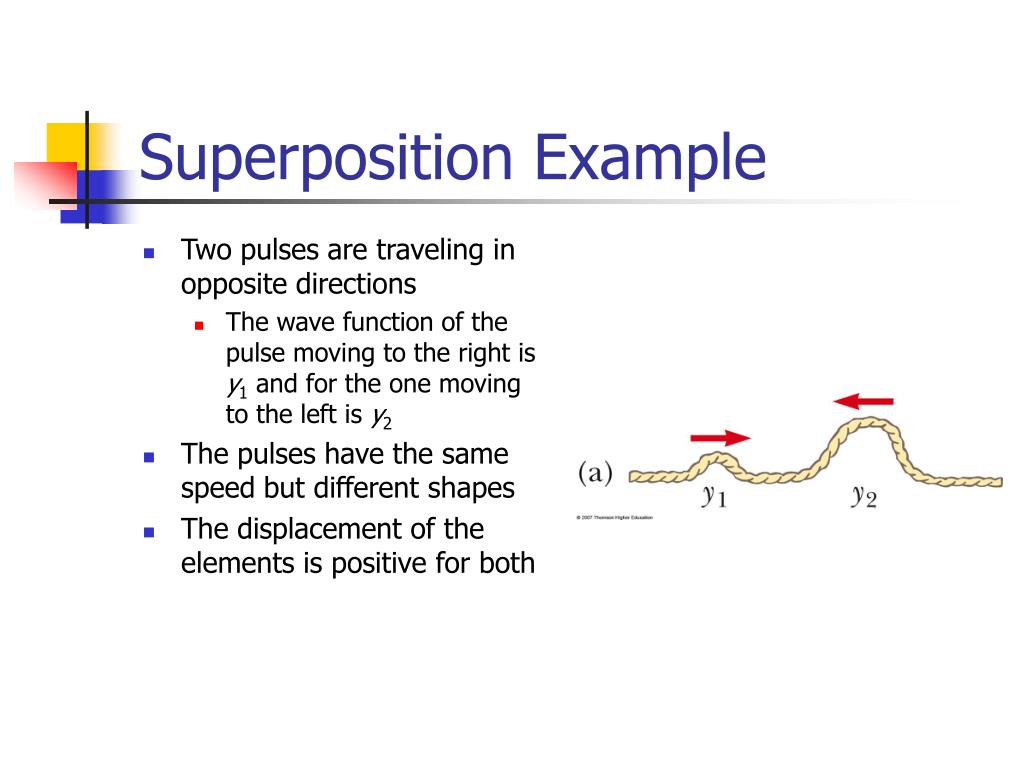
In computing, superposition of multiple code paths, code and data, or multiple data structures is sometimes seen in shared memory, fat binaries, as well as overlapping instructions in highly optimized self-modifying code and executable text.Īccording to Léon Brillouin, the principle of superposition was first stated by Daniel Bernoulli in 1753: "The general motion of a vibrating system is given by a superposition of its proper vibrations." The principle was rejected by Leonhard Euler and then by Joseph Lagrange.The resultant displacement of a number of waves in a medium at a particular point is the vector sum of the. In music, theorist Joseph Schillinger used a form of the superposition principle as one basis of his Theory of Rhythm in his Schillinger System of Musical Composition. According to the principle of superposition.The superposition principle can be applied when small deviations from a known solution to a nonlinear system are analyzed by linearization.In process control, the superposition principle is used in model predictive control.This principle is used in the analytic element method to develop analytical elements capable of being combined in a single model. The resultant electric field is a vector sum of the electric field due to individual charges. The principle of superposition states that every charge in space creates an electric field at point independent of the presence of other charges in that medium.
In hydrogeology, the superposition principle is applied to the drawdown of two or more water wells pumping in an ideal aquifer. As illustrated in Cartesian coordinates by (4.2.3), Poissons equation is a linear second-order differential equation relating. The principle of superposition allows for the combination of two or more electric fields.

Mode superposition method uses the natural frequencies and mode shapes to characterize the dynamic response of a linear structure. In engineering, superposition is used to solve for beam and structure deflections of combined loads when the effects are linear (i.e., each load does not affect the results of the other loads, and the effect of each load does not significantly alter the geometry of the structural system).The principle also applies to other linear differential equations arising in physics, such as the heat equation. Thus, the superposition principle can be used to simplify the computation of fields that arise from a given charge and current distribution. In physics, Maxwell's equations imply that the (possibly time-varying) distributions of charges and currents are related to the electric and magnetic fields by a linear transformation.For another, a related technique in circuit analysis, see Superposition theorem. The use of Fourier analysis on this basis is particularly common. Thus, a superposition (i.e., sum) of input signals will yield the superposition of the responses. In electrical engineering, in a linear circuit, the input (an applied time-varying voltage signal) is related to the output (a current or voltage anywhere in the circuit) by a linear transformation.This decomposition can help to simplify controller design.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
